Configure EtherChannel
Configuration
Configuring EtherChannel involves grouping multiple physical Ethernet ports into one logical interface, known as a port channel. On Cisco switches, this is done using the channel-group command within interface configuration mode (Cisco Configuration Guide). Each physical interface that will participate in the EtherChannel must be added to the same channel group and share consistent settings such as speed, duplex, VLAN membership, and trunking mode. For example, look at the figure to the right. In this example, there are three main steps to setup EtherChannel between S1 and S2.
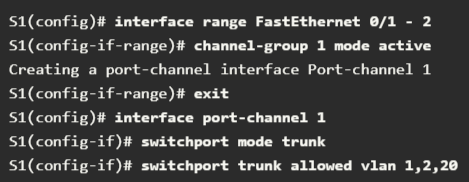
1. Specify the interfaces that compose the EtherChannel group using the interface range interface global configuration command.
2. Create the port channel interface with the channel-group identifier mode active command in interface configuration mode. The identifier specifies a channel group number. The mode active part identifies this as an LACP EtherChannel configuration.
3. To change Layer 2 settings on the port channel interface, enter port channel interface configuration mode using the interface port-channel command, followed by the interface identifier. In this example, S1 is configured with an LACP EtherChannel. The port channel is configured as a trunk interface with the allowed VLANs separated.
Once these steps are completed on both switches, the EtherChannel will form, and the bundled links will operate as a single logical connection (NetworkLessons.com). This not only simplifies management but also increases bandwidth and provides redundancy. EtherChannel is a powerful tool in switch-to-switch communication that improves network performance and reliability.